Have You Ever Wondered Why Don’t Humans Have Tails?
You may have noticed that humans don’t have tails, unlike many other animals. But have you ever wondered why? Scientists believe it’s due to our unique evolutionary history. Let’s dive into the reasons behind this fascinating phenomenon!
Why Animals Have Tails
Tails serve many important functions in animals, such as balance, communication, and defense. For instance, monkeys use their tails to help balance when climbing trees. However, humans have evolved different ways to perform these functions without the need for a tail.
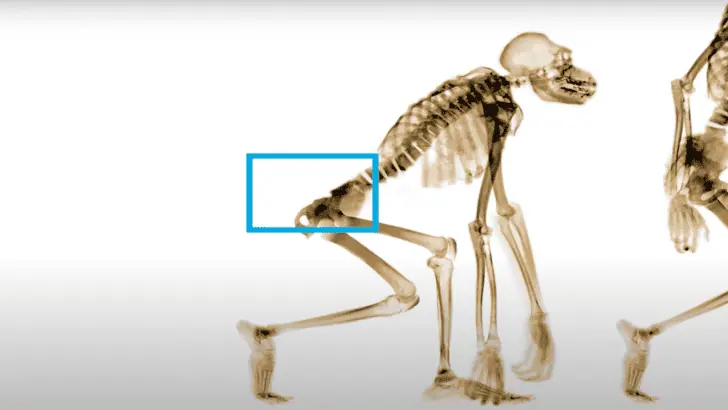
Evolutionary Background
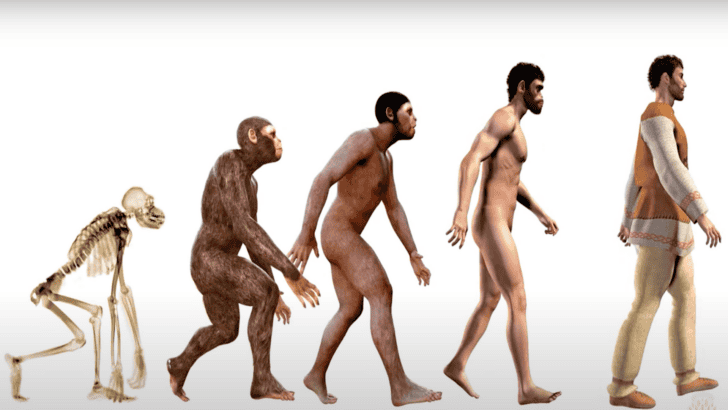
Millions of years ago, early human ancestors had tails. As time passed and humans began spending more time on the ground instead of in trees, the need for tails gradually diminished. This shift eventually led to the disappearance of tails in humans, and our species transitioned from walking on four legs to walking on two.
The Development of the Coccyx
The coccyx, or tailbone, is a small, triangular bone at the base of the human spine. It’s a remnant of the tail that our ancestors once had. While the coccyx no longer serves a functional purpose, it is a vestigial structure that provides insight into our evolutionary past.
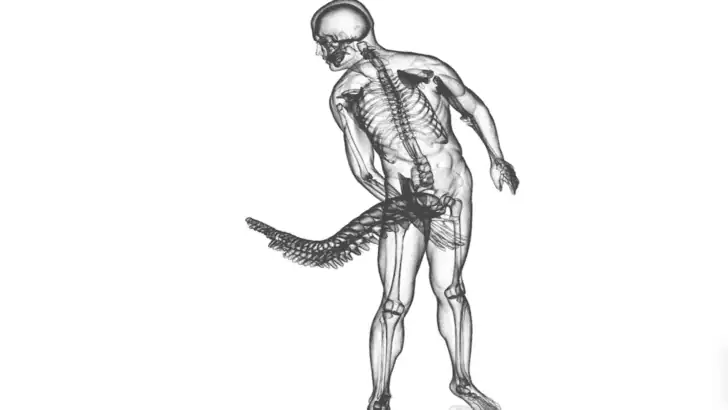
Genetic Factors
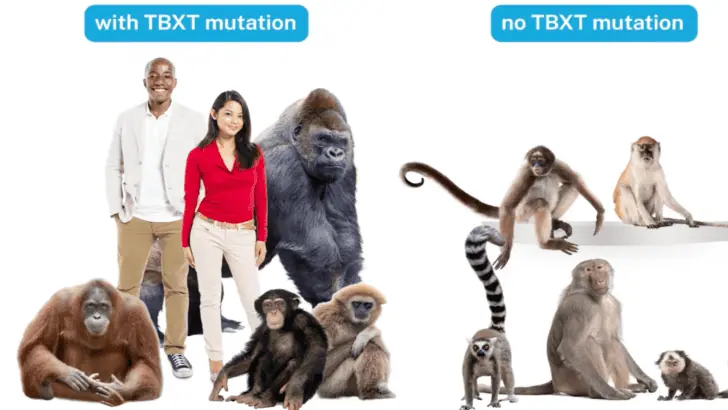
The absence of tails in humans can be traced to specific genetic changes, such as the alu mutation. This mutation occurred millions of years ago and was passed down through generations. Today, this mutation is clearly identified in humans and other tailless species.
Evolutionary Advantages
Losing the tail provided early humans with certain evolutionary advantages. It facilitated upright walking and running, which were important for survival. It also allowed for more complex social and physical behaviors. Personally, I’m glad we don’t have tails – I’m sure I’d find a way to trip over it!

Comparison with Other Primates
While humans have lost their tails, many primates still have them. These tails are crucial for their arboreal lifestyles, helping animals like spider monkeys and gibbons balance and grip in trees. The absence of tails in humans marks a significant divergence from our primate relatives.
Rare Cases of Human Tails
Though rare, some humans are born with small, benign tail-like structures. These tails are usually removed shortly after birth to avoid complications later on. These instances, though uncommon, serve as reminders of our evolutionary past.

Tails in Human Culture
Although humans don’t have tails, they still appear in myths and folklore. Tails are often depicted as symbols of animalistic traits or supernatural powers. This shows how the idea of tails has persisted in the human imagination, particularly in movies and comics.
Conclusion
The absence of tails in humans offers fascinating insight into our evolutionary history. It highlights how our species has adapted over millions of years, providing a broader understanding of human evolution. Understanding why we don’t have tails is part of the larger story of who we are as humans.